DIETARY GUIDANCE
Eating well
Healthy eating is about consuming the right amount of food for your energy needs and the right balance of foods to make sure your body gets all the nutrients it needs.
Across Latin America, food and nutrition guidelines have been developed by public health authorities to promote a healthy balanced diet, encourage regular physical activity and consider cultural and dietary factors. Many of these have an illustrative summary of the main food groups and their recommended proportions for a healthy diet to help you see how you can get the balance of energy and nutrients, and how foods can often sit together in the same group or can be swapped. It’s appreciated you may not be able to achieve the balance shown with every meal, but the principle is to try and get the balance over a day or even a week. These guidelines tend to be based on an average calorie intake of 2000Kcal for adult females and 2500 Kcals for adult males and includes all food and drinks.
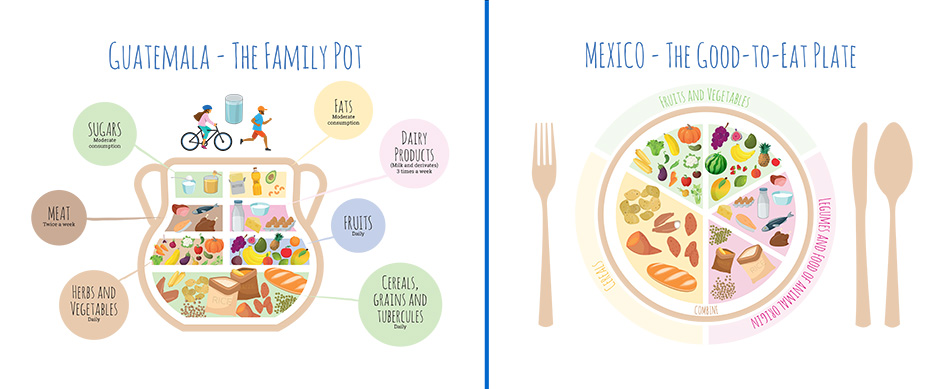
The country guidelines across the region typically have very similar principles in terms of guidance, such as:
- Most of us are still not eating enough fruit and vegetables and should make up over a third of what we eat each day; aim to eat at least five portions each day. Fruit and vegetables are a good source of vitamins, minerals and fibre.
- Choose starchy foods with higher fibre wholegrain varieties and base meals on potatoes, bread, rice, pasta or other starchy carbohydrates.
- Have some dairy or dairy alternative products (such as soya drinks and yoghurts). Milk, cheese and yoghurt are good sources of protein and some vitamins, and they are also an important source of calcium.
- Aim to eat at least two portions of fish every week, one of which should be oily, such as salmon or mackerel if possible.
- Choose lean cuts of meat and mince and eat less red and processed meat where possible. Pulses, such as beans, peas and lentils are also good alternatives to meat as they are low in fat and high in fibre and protein.
- Choose unsaturated oils and spreads and eat in small amounts.
- Eat foods high in fat, salt and sugar less often and in small amounts, these foods include items such as chocolate, cakes, biscuits, soft drinks, butter and ice-cream.
- Stay hydrated and drink plenty of fluids with up to 6-8 cups or glasses of water a day. Avoid excessive consumption of soft drinks and sugary juices.
- Try and increase your daily physical activity and sport. The important thing to consider is the amount of physical activity (duration) as well as the intensity and frequency.
For more detailed advice on diet and lifestyle, please visit below guidelines from across the region:
| Argentina | Ministry of Health |
| Bolivia | Ministry of Health |
| Brazil | Ministry of Health |
| Chile | Ministry of Health |
| Columbia | Ministry of Health |
| Costa Rica | Ministry of Health |
| Cuba | Ministry of Health |
| Dominican Republic | Ministry of Public Health |
| Ecuador | Ministry of Public Health |
| El Salvador | Ministry of Health / Pan American Health Organisation |
| Guatemala | Ministry of Health |
| Mexico | Ministry of Health |
| Nicaragua | Ministry of Health |
| Panamá | Ministry of Health |
| Paraguay | Ministry of Health |
| Perú | Ministry of Health |
| Puerto Rico | USDA / US Department of Health / Food and Nutrition Commission for Puerto Rico Food & Drink Commission |
| Uruguay | Ministry of Social Development |
| Venezuela | Ministry of Health |
| SUGAR FACTS |
|---|
| Sugar has four calories per gram compared to protein (four calories), alcohol (seven calories) and fat (nine calories). |
| White and brown sugars are both made from sugar cane or sugar beet. Brown sugar contain molasses, which provides the dark colour, characteristic flavour and texture. The darker brown the sugar, the higher the amount of molasses. |