BALANCED DIET
No single food or drink contains all the essential nutrients your body needs, which is why variety is key. The World Health Organization (1) has a number of basic principles of what constitutes a healthy diet to help prevent non-communicable diseases, although the exact make-up of your diet can vary depending on your age, gender, lifestyle, levels of physical activity, cultural context and available foods and dietary customs.
It’s also important to balance the energy you take in as food and drinks (measured in calories), by the energy you use up through physical activity.
THE WHO’S BASIC DIET PRINCIPLES
-
Fruit and vegetables - eating at least 440g or five portions daily
-
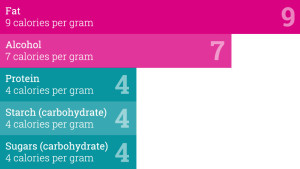
Fats - reducing the amount of total fat intake to less than 30% of total energy intake
-
Dairy, salt, sodium and potassium - reduce salt intake to less than 5g per day
-
Sugars - reduce to less than 10% of total energy intake. A further reduction to less than 5% of total energy intake is suggested for additional health benefits.